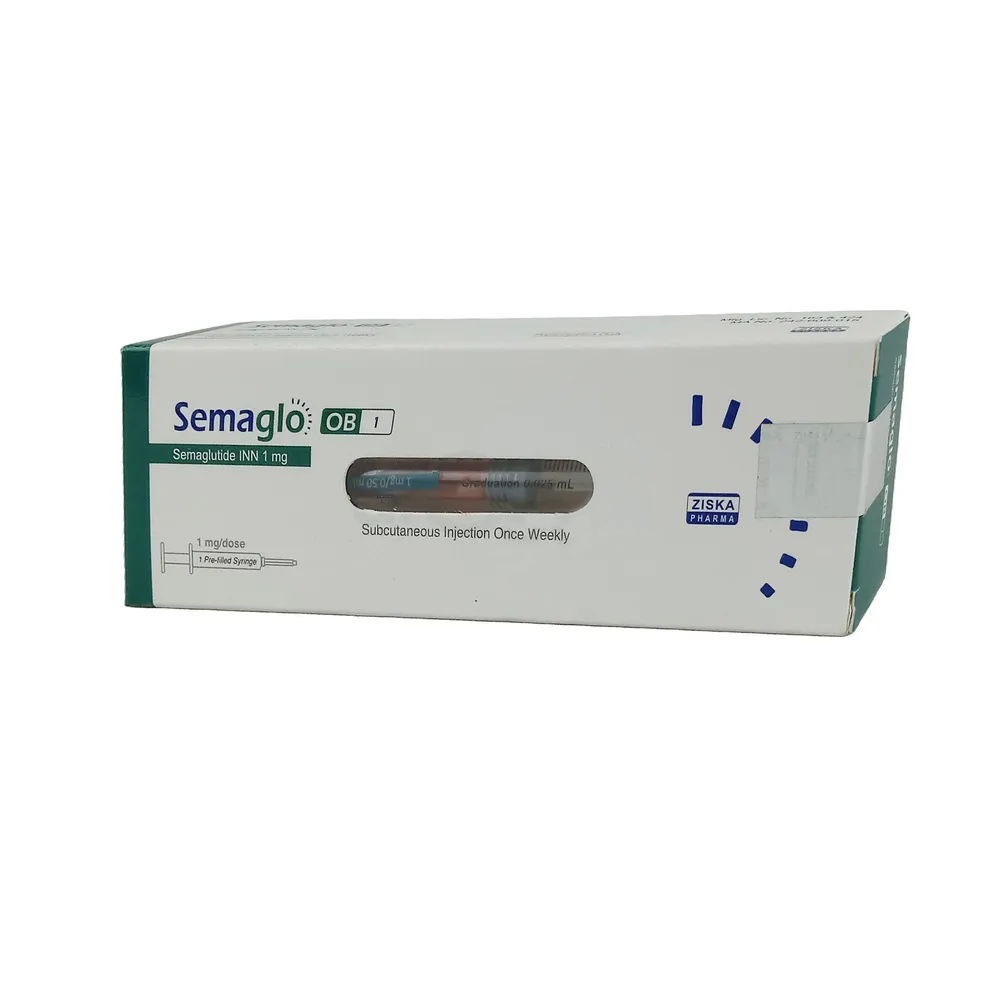
1 mg pre-filled syringe:
৳ 1,000.00
Also available as:
Indications
For Diabetes: Semaglo OB is indicated in-
- An adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- To reduce the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus and established cardiovascular disease
- 30 kg/m2 or greater (Obesity) or
- 27 kg/m2 or greater (Overweight) in the presence of at least one weight-related comorbid condition (e.g. hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus or dyslipidemia).
Pharmacology
Semaglutide is a GLP-1 analogue with 94% sequence as same as to human GLP-1. Semaglutide acts as a GLP-1 receptor agonist that selectively binds to and activates the GLP-1 receptor. Semaglutide reduces blood glucose in a glucose dependent manner by stimulating insulin secretion and lowering glucagon secretion when blood glucose is high. The mechanism of blood glucose lowering also involves a minor delay in gastric emptying. During hypoglycemia, Semaglutide diminishes insulin secretion and does not impair glucagon secretion. Semaglutide reduces body weight and body fat mass by an overall reduced appetite.
Dosage & Administration
For Diabetes:
Semaglutide Tablet: Take Semaglutide at least 30 minutes before the first food, beverage, or other oral medications of the day with no more than 4 ounces (118 ml) of plain water only.
Switching patients between Semaglutide injection and Semaglutide tablet-
For Obesity: The starting dose is 0.25 mg Semaglutide once weekly for 4 weeks subcutaneously. If patients do not tolerate a dose during dose escalation, consider delaying dose escalation for 4 weeks. If patients do not tolerate the maintenance dose 2.4 mg, the dose can be temporarily decreased to 1.7 mg once weekly for maximum 4 weeks. After 4 weeks increase the dose to 2.4 mg. Weekly doses higher than 2.4 mg is not recommended. Semaglutide is to be administered once weekly at any time of the day with or without meals. Semaglutide is to be injected subcutaneously in the abdomen, thigh or in upper arm. The injection site can be changed without dose adjustment. Semaglutide should not be administered intravenously or intramuscularly. The day of weekly administration can be changed if necessary as long as the time between two doses is at least 2 days (>48 hours). After selecting a new dosing day, once weekly dosing should be continued.
Semaglutide Tablet: Take Semaglutide at least 30 minutes before the first food, beverage, or other oral medications of the day with no more than 4 ounces (118 ml) of plain water only.
- Starter Dose: Start Semaglutide with 3 mg once daily for 30 days
- Maintenance Dose: After 30 days on the 3 mg dose, increase the dose to 7 mg once daily
- For Additional Glycemic Control: If additional glycemic control is needed after at least 30 days on the 7 mg dose, the dose can be increased to 14 mg once daily
Switching patients between Semaglutide injection and Semaglutide tablet-
- Patients treated with once weekly Semaglutide injection 0.5 mg subcutaneous injection can be transitioned to Semaglutide 7 mg or 14 mg tablet. Patients can start Semaglutide tablet up to 7 days after their last injection of Semaglutide injection. There is no equivalent dose of Semaglutide tablet for Semaglutide injection 1 mg
- Patients treated with Semaglutide 14 mg tablet daily can be transitioned to Semaglutide subcutaneous injection 0.5 mg once weekly. Patients can start Semaglutide injection the day after their last dose of Semaglutide tablet.
For Obesity: The starting dose is 0.25 mg Semaglutide once weekly for 4 weeks subcutaneously. If patients do not tolerate a dose during dose escalation, consider delaying dose escalation for 4 weeks. If patients do not tolerate the maintenance dose 2.4 mg, the dose can be temporarily decreased to 1.7 mg once weekly for maximum 4 weeks. After 4 weeks increase the dose to 2.4 mg. Weekly doses higher than 2.4 mg is not recommended. Semaglutide is to be administered once weekly at any time of the day with or without meals. Semaglutide is to be injected subcutaneously in the abdomen, thigh or in upper arm. The injection site can be changed without dose adjustment. Semaglutide should not be administered intravenously or intramuscularly. The day of weekly administration can be changed if necessary as long as the time between two doses is at least 2 days (>48 hours). After selecting a new dosing day, once weekly dosing should be continued.
Interaction
With medicine: Semaglo OB delays gastric emptying which may influence the absorption of other oral medications. Trials were conducted to study the potential effect of Semaglo OB on the absorption of oral medicinal products taken with Semaglo OB administered orally at steady state exposure.
With food & others: Concomitant intake of food reduces the exposure of Semaglo OB.
With food & others: Concomitant intake of food reduces the exposure of Semaglo OB.
Contraindications
- Semaxen is contraindicated in patients who are hypersensitive to Semaxen or to any ingredient in the formulation, including any non-medicinal ingredient, or component of the container.
- Semaxen is contraindicated in patients who have a personal or family history of Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma (MTC) or in patients with Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2).
- Semaxen should not be used during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
Side Effects
Common side effects: Vomiting, stomach upset or indigestion inflamed stomach, reflux or heartburn or GERD, stomach pain, bloating of the stomach, constipation, change in the way food or drink tastes, tiredness, less appetite, gas (flatulence), increase of pancreatic enzymes (such as lipase and amylase).
Rare side effects: Serious allergic reactions (anaphylactic reactions). You should seek immediate medical help and inform your doctor straight away if you get symptoms such as breathing problems, swelling of face and throat, wheezing, fast heartbeat, pale and cold skin, feeling dizzy or weak.
Rare side effects: Serious allergic reactions (anaphylactic reactions). You should seek immediate medical help and inform your doctor straight away if you get symptoms such as breathing problems, swelling of face and throat, wheezing, fast heartbeat, pale and cold skin, feeling dizzy or weak.
Pregnancy & Lactation
Pregnancy: The extent of exposure in pregnancy during clinical trials was very limited and there are no adequate and well controlled studies of Semaglutide in pregnant women. Therefore, Semaxen should not be used during pregnancy. If a patient wishes to become pregnant, or pregnancy occurs, Semaxen should be discontinued. Semaxen should be discontinued at least 2 months before a planned pregnancy due to the long half-life of Semaglutide.
Lactation: There are no data on the presence of Semaglutide in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Because of the unknown potential for serious adverse reactions in the breastfed infant due to the possible accumulation of salcaprozate sodium (SNAC), an absorption enhancer in Semaxen, from breastfeeding and because there are alternative formulations of Semaglutide that can be used during lactation, advise patients that breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with Semaxen. Discontinue Semaxen in women at least 2 months before a planned pregnancy due to the long washout period for Semaglutide.
Lactation: There are no data on the presence of Semaglutide in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Because of the unknown potential for serious adverse reactions in the breastfed infant due to the possible accumulation of salcaprozate sodium (SNAC), an absorption enhancer in Semaxen, from breastfeeding and because there are alternative formulations of Semaglutide that can be used during lactation, advise patients that breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with Semaxen. Discontinue Semaxen in women at least 2 months before a planned pregnancy due to the long washout period for Semaglutide.
Precautions & Warnings
Should not be used in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus or for the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis. Patients should be advised to take precautions to avoid hypoglycemia while driving and using machines. Semaglo OB causes an increase in heart rate. Caution should be observed in patients who have cardiac conditions that might be worsened by an increase in heart rate, such as tachyarrhythmias. Patients treated with Semaglo OB in combination with an insulin secretagogue (e.g., sulfonylureas) or insulin may have an increased risk of hypoglycemia. The risk of hypoglycemia may be lowered by reducing the dose of the secretagogue or insulin when initiating treatment with Semaxen.
Use in Special Populations
Pediatric population: The safety and efficacy of Semaglo OB in children and adolescents below 18 years have not yet been established. No data are available.
Elderly: No dose adjustment is required based on age.
Renal impairment: No dose adjustment is required for patients with mild moderate or severe renal impairment. Semaglo OB is not recommended for use in patients with end-stage renal disease.
Hepatic impairment: No dose adjustment is required for patients with hepatic impairment. Caution should be exercised when treating these patients with Semaglo OB.
Elderly: No dose adjustment is required based on age.
Renal impairment: No dose adjustment is required for patients with mild moderate or severe renal impairment. Semaglo OB is not recommended for use in patients with end-stage renal disease.
Hepatic impairment: No dose adjustment is required for patients with hepatic impairment. Caution should be exercised when treating these patients with Semaglo OB.
Overdose Effects
Overdose: Overdose of up to 4 mg in a single dose and up to 4 mg in a week have been reported in clinical trials. The most commonly reported adverse reaction was nausea. There is no specific antidote for overdose with Semaglo OB. In the event of overdose appropriate supportive treatment should be initiated according to the patients clinical sign and symptoms.
Dose adjustment: When Semaglo OB is added to existing metformin and/or thiazolidinedione therapy, the current dose of metformin and/or thiazolidinedione can be continued unchanged. When Semaglo OB is added to existing therapy of sulfonylurea or insulin, a reduction in the dose of sulfonylurea or insulin should be considered to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia. Self-monitoring in blood glucose is not needed in order to adjust the dose of Semaglo OB. Blood glucose self-monitoring is necessary to adjust the dose of sulfonylurea and insulin particularly when Semaglo OB is started and insulin is reduced.
Missed dose: If a dose is missed, it should be administered as soon as possible and within 5 days after the missed dose. If more than 5 days have passed, the missed dose should be skipped and the next dose should be administered on the regular scheduled day. In each case, patients can then resume their regular once weekly dosing schedule.
Dose adjustment: When Semaglo OB is added to existing metformin and/or thiazolidinedione therapy, the current dose of metformin and/or thiazolidinedione can be continued unchanged. When Semaglo OB is added to existing therapy of sulfonylurea or insulin, a reduction in the dose of sulfonylurea or insulin should be considered to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia. Self-monitoring in blood glucose is not needed in order to adjust the dose of Semaglo OB. Blood glucose self-monitoring is necessary to adjust the dose of sulfonylurea and insulin particularly when Semaglo OB is started and insulin is reduced.
Missed dose: If a dose is missed, it should be administered as soon as possible and within 5 days after the missed dose. If more than 5 days have passed, the missed dose should be skipped and the next dose should be administered on the regular scheduled day. In each case, patients can then resume their regular once weekly dosing schedule.
Therapeutic Class
GLP-1 receptor agonists
Storage Conditions
Injection: Store at 2°C to 8°C (in a refrigerator). Do not freeze. Keep away from light. Keep all the medicine out of the reach of children.
Tablet: Store below 30°C, in a cool and dry place. Keep away from light. Keep all the medicine out of the reach of children.
Tablet: Store below 30°C, in a cool and dry place. Keep away from light. Keep all the medicine out of the reach of children.